Introduction to Commitment Orchestrator (Beta)
Currently, Commitment Orchestrator is behind the feature flags CCM_COMMORCH and CCM_COMM_SETUP. Contact Harness Support to enable the feature.
In recent years, organizations leveraging cloud services have witnessed a notable trend - the steady increase in cloud costs. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud or expand their existing cloud infrastructure, the expenses associated with cloud infrastructure, storage, and data processing have become a significant portion of their overall expenditures.
This rise in cloud costs reflects the growing scale of business operations in the cloud environment, as many organizations transition from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based solutions or ramp up their existing cloud utilization. It signifies the expanding scope and investment in cloud services.
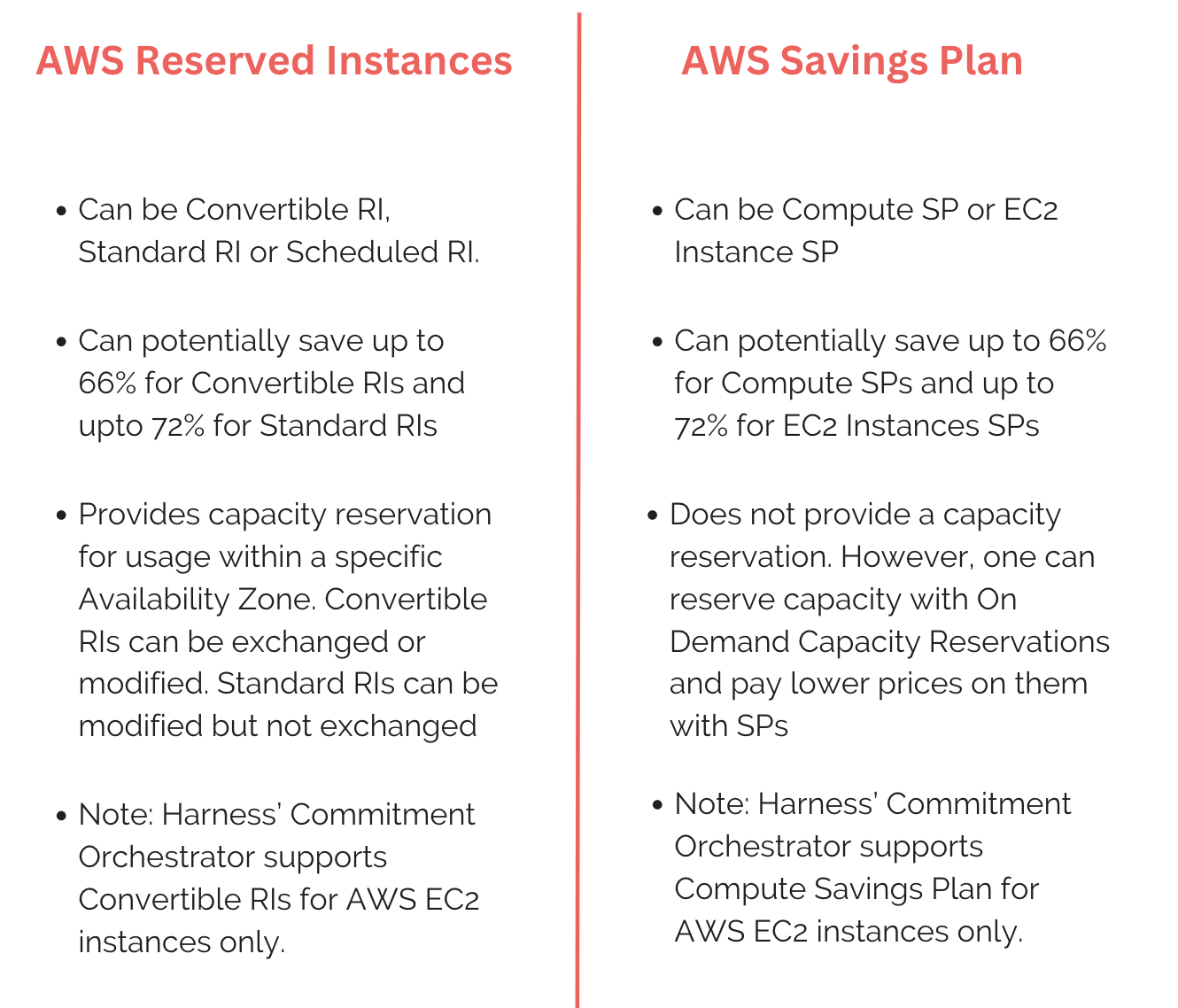
To help bring down the cloud costs, providers often offer special discounted rates against on-demand costs to the customers. These commitments are mostly in form of RI (Reserved Instances) or SPs(Savings Plan).
-
Reserved Instances: Reserved Instances are a pricing model offered by cloud service providers that allows customers to reserve and commit to a specific amount of computing capacity in advance for a term of one or three years. This commitment comes with a significant discount compared to on-demand pricing, making it a cost-effective option for workloads with predictable and sustained usage.
-
Savings Plans: Savings Plans are a flexible pricing model introduced by cloud service providers that offer customers significant discounts on their usage in exchange for committing to a consistent amount of usage, measured in dollars per hour, for a one- or three-year term. Unlike Reserved Instances, Savings Plans offer more flexibility in terms of instance type, region, and operating system, making them suitable for workloads with variable usage patterns.
Here's how Savings Plans are referred to by major cloud providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): In the context of AWS, Savings Plans are known as Savings Plans.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure refers to its equivalent of Savings Plans as Azure Reserved VM Instances (RIs) or Azure Reserved Capacity.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP's counterpart to Savings Plans is called Committed Use Discounts (CUDs) or Committed Use Contracts (CUCs).
It's essential for organizations to carefully analyze their usage patterns before making commitments to ensure they choose the most suitable Reserved Instances for their needs.
Commitments in the cloud, such as Reserved Instances (RIs) or other long-term contracts, can pose challenges in various situations if not managed correctly. To highlight a few:
- If the organization's workload patterns or compute spend changes significantly due to policy or market factors, commitments made based on initial assumptions may no longer align with actual resource needs.
- Rapid changes in technology or the adoption of new services may render existing commitments less cost-effective or even obsolete.
- Overcommitting to a specific cloud provider or service may lead to vendor lock-in, making it challenging to switch to a different provider or adopt a multi-cloud strategy.
- Economic or business uncertainties can make long-term commitments risky, especially if there's a chance of downsizing or changes in strategy.
- Some commitments, such as rigid long-term contracts, may lack flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances or unexpected events.
- Overcommitting resources may result in underutilization, leading to inefficient use of commitments and potentially higher overall costs due to unnecessary commitment plans.
- While managing commitments, there's always overhead in understanding the context of the need of purchase and to identify what to purchase next among the multiple options for commitments, It requires continuous manual effort and is a lot more human error prone in case of wrong predictions.
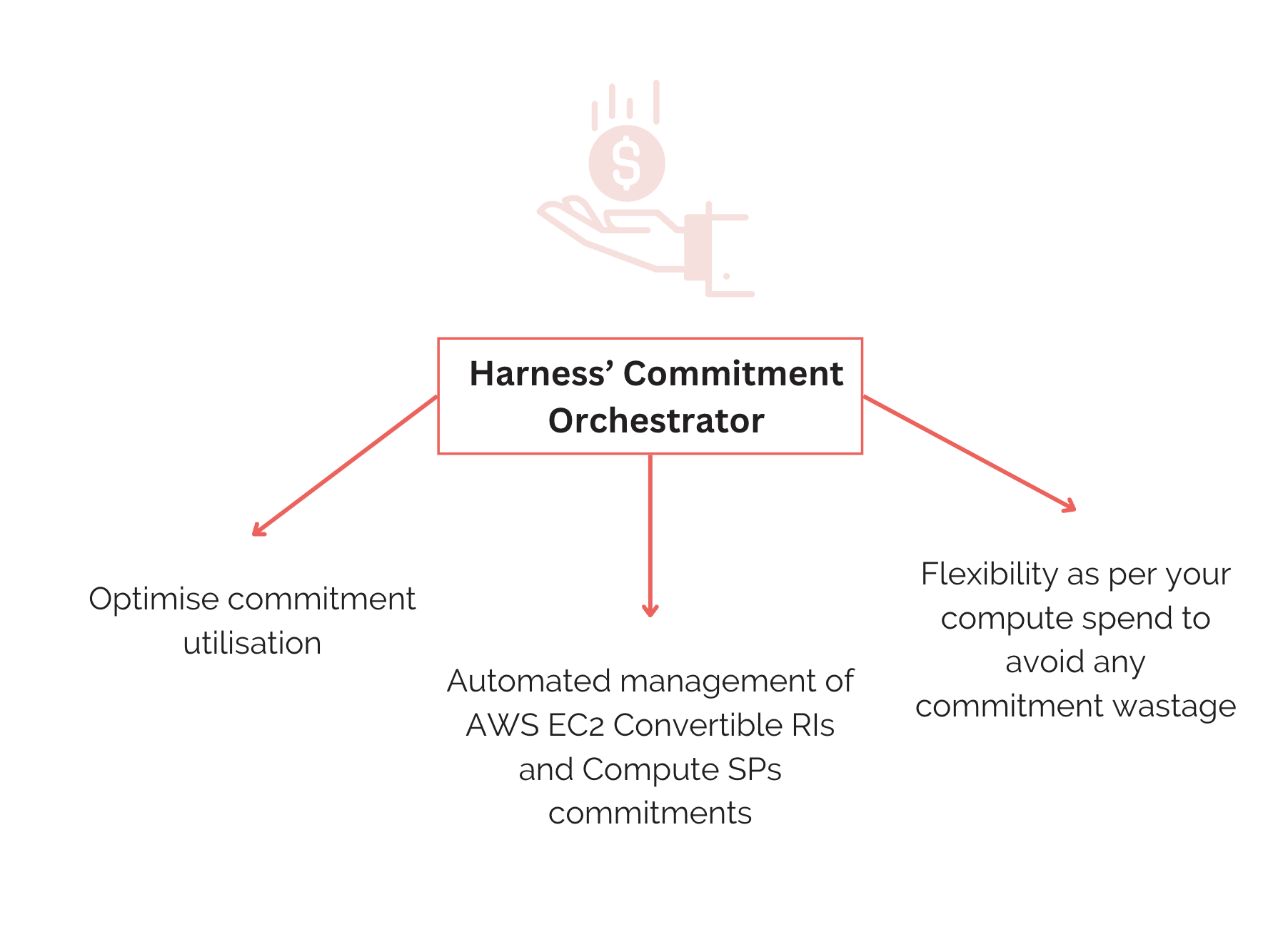
At Harness, we are committed to bring in the power of AI and ML to manage the commitments. Harness CCM helps you to track everything about your cloud spends so that you have an optimized cloud spend. With our latest addition of Commitment Orchestrator for AWS EC2 Convertible RIs and Compute Savings Plans, we focus on managing your commitments for optimal performance and mitigating the problems associated with manual management of commitments.
What is over commitment and under commitment?
In the context of cloud spend or cloud bills breakdown,, over-commitment and under-commitment typically refer to the utilization of resources compared to the commitments made through discount plans like Reserved Instances (RIs) or Savings Plan (SPs).
Over-Commitment:
Over-commitment occurs when an organization has reserved more resources (such as instances or capacity) or bought extra Savings Plans to cover their compute spend than it actually needs or utilizes. For example, an organization may have purchased a significant number of Reserved Instances based on an initial estimation of their workload. If the actual usage turns out to be lower than expected, the resources deployed are considered to be over-committed, leading to wastage and underutilization.
While over-commitment may provide some level of capacity assurance, it can result in underutilized resources, leading to higher costs than necessary. The committed resources are paid for upfront or over the term, regardless of whether they are fully utilized.
Under-Commitment:
Under-commitment occurs when an organization hasn't reserved enough resources or bought enough Savings Plans to meet its actual demand or workload. For instance, an organization may have opted for pay-as-you-go (on-demand) pricing or may not have purchased enough Reserved Instances to cover its workload. This results in a situation where resources are provisioned on-demand, potentially leading to higher costs per unit of compute compared to the reserved pricing.
Under-commitment can result in higher overall costs due to the absence of reserved capacity discounts. It may also lead to unpredicted extra costs during peak demand periods when on-demand resources might be more expensive.
Finding the right balance between over-commitment and under-commitment is a key aspect of effective commitment management in the cloud.
How does a Commitment Orchestrator help with under commitments or overcommitments?
Harness's Commitment Orchestrator is a specialized tool designed to assist organizations in effectively managing their cloud commitments. Here's how Harness's Commitment Orchestrator can help manage commitments:
- Automated commitment purchasing and management: The Commitment Orchestrator automates the process of purchasing cloud commitments such as Reserved Instances (RIs) or Savings Plans (SPs). It analyzes historical usage data and future workload projections to recommend the most cost-effective commitment options. With our upcoming forecasting feature, organizations will have better control over their commitments.
- Maximize savings from commitments: Harness's Commitment Orchestrator employs advanced algorithms and optimization techniques to maximize cost savings from cloud commitments.
- Maximize compute coverage: This feature ensures comprehensive coverage of compute resources under commitments. Harness's Commitment Orchestrator analyzes resource utilization patterns and recommends commitments that align with the organization's compute requirements while minimizing underutilization.
- Optimize commitment utilization: The Commitment Orchestrator continuously monitors and analyzes commitment utilization. It identifies underutilized commitments or opportunities for optimization so you can reallocate resources or adjust commitments to maximize utilization and cost-effectiveness.
- Compliance at scale with RBAC, audit trails, OPA: Harness's Commitment Orchestrator provides robust Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) mechanisms to define and enforce granular access controls and permissions within the platform. It maintains detailed audit trails of all activities and changes performed within the platform, ensuring compliance with policies and regulations. Harness's Commitment Orchestrator also supports Open Policy Agent (OPA) integration, allowing organizations to define and enforce custom policies for commitment management.
How does Commitment Orchestrator do this?
Commitment Orchestrator does all of this with the help of its 2 engines: Utilisation engine and Purchase engine
| Utilisation engine | Purchase engine |
|---|---|
| The utilization engine leverages machine learning (ML) and intelligent analysis of existing usage patterns to optimize resource utilization and increase the efficiency of underutilized Reserved Instances (RIs) or Savings Plan.. It breaks RIs into the smallest units and assembles them to meet target instance types. By intelligently analyzing these patterns, the engine identifies opportunities for optimization that can lead to significant cost savings for the business. | The purchase engine analyzes the on-demand spend and then purchases the RIs/SPs basis the target coverage. |
Getting Started
Commitment Orchestrator can be found on our dashboard under Cloud Costs module. Commitment Orchestrator can be easily setup from the dashboard itself by following these steps:
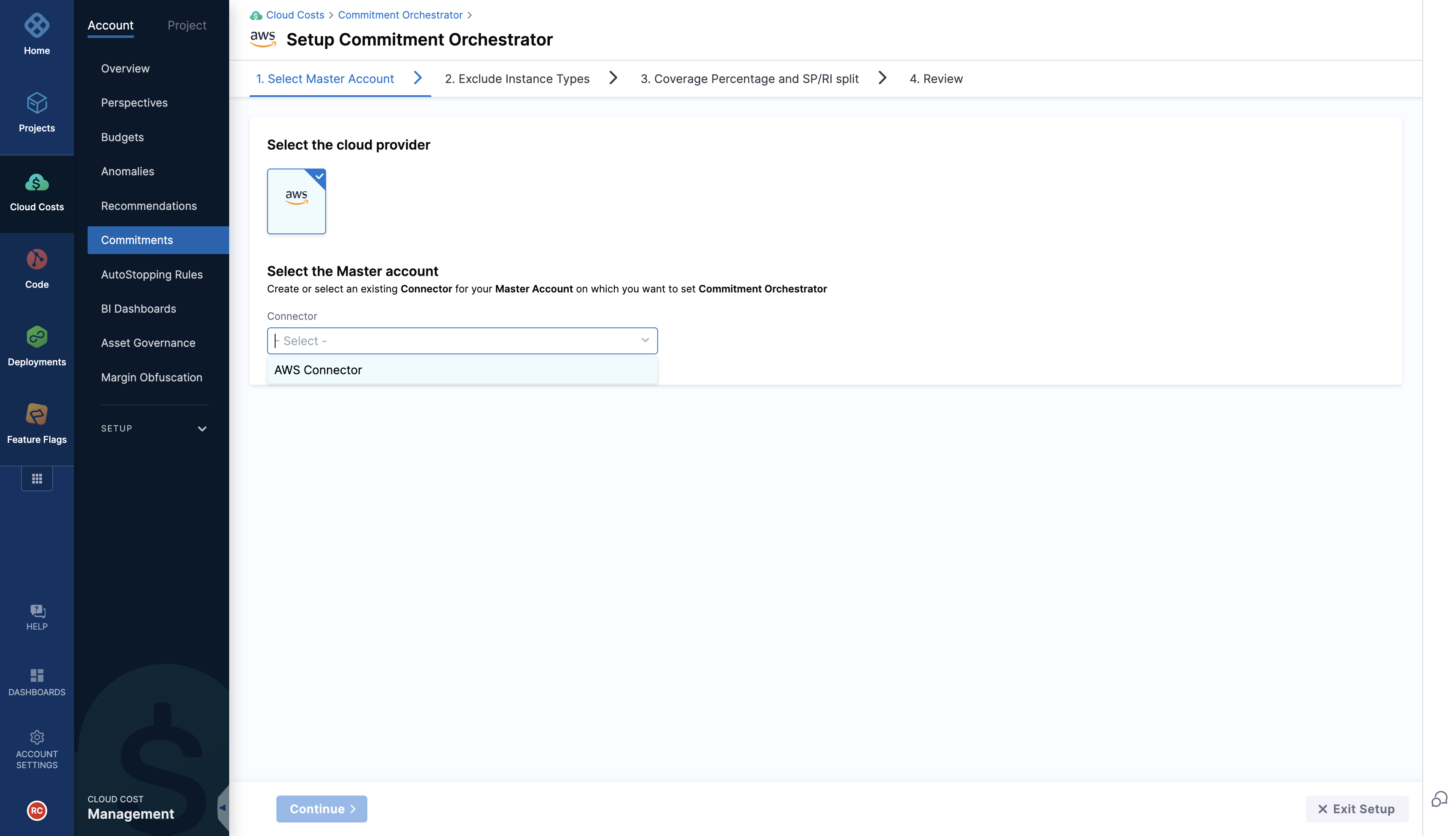
Step 1 : Setting up the master account
You need to select the master account with the right permissions to be added via connector on which you want to enable orchestration. You can either select an existing connector for your master account or create one.
Step 2: Exclude Instance types
Commitment Orchestrator provides you with an option to choose the instances you would like to exclude when orchestrating instances for Compute Usage.
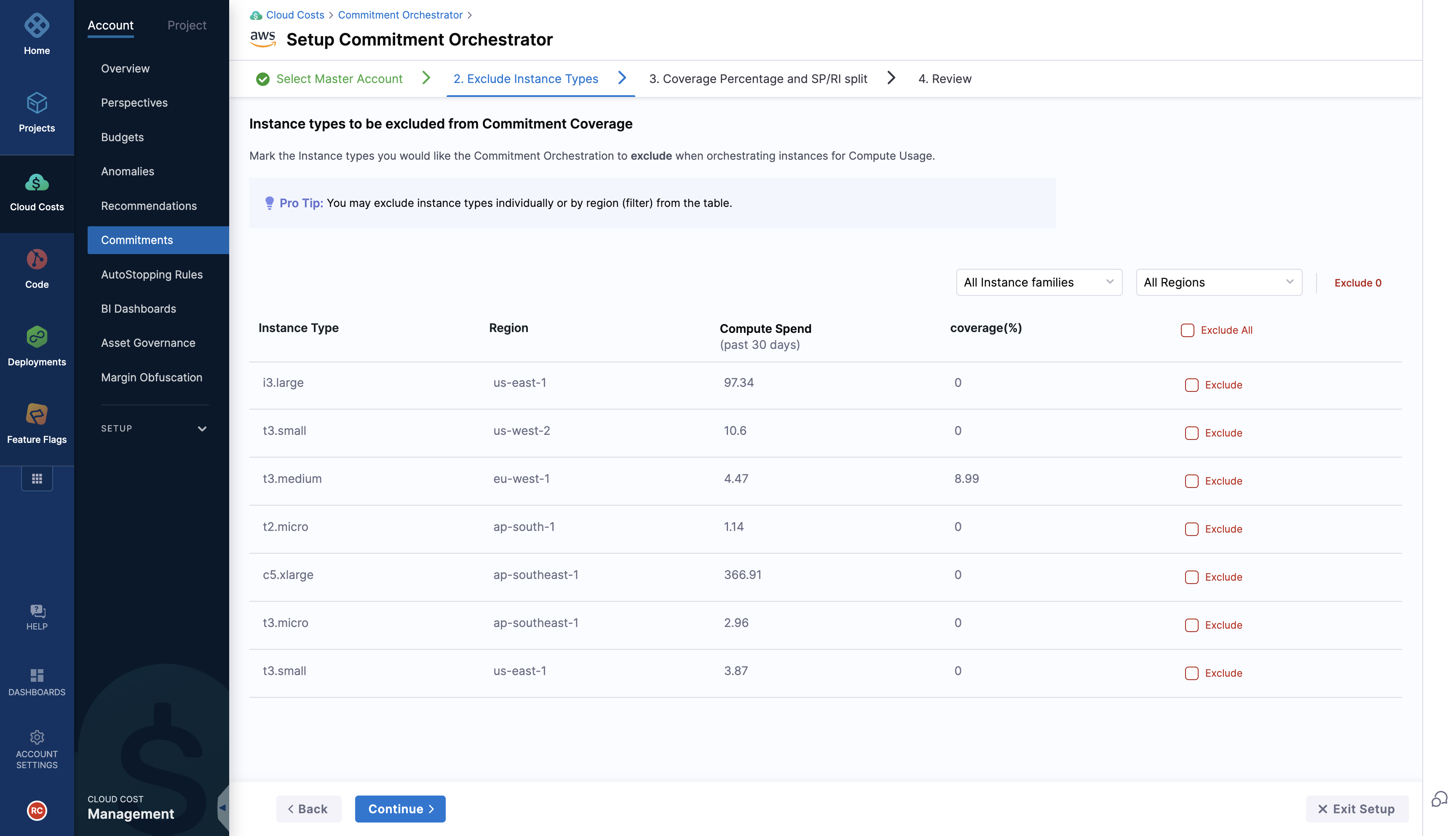
The purchases will happen only at master account level and thus will be in turn applicable for child accounts as well. The exclusion list will only be considered for the compute spend calulations and actual RI/SP may be used against the instances if they are part of child accounts.
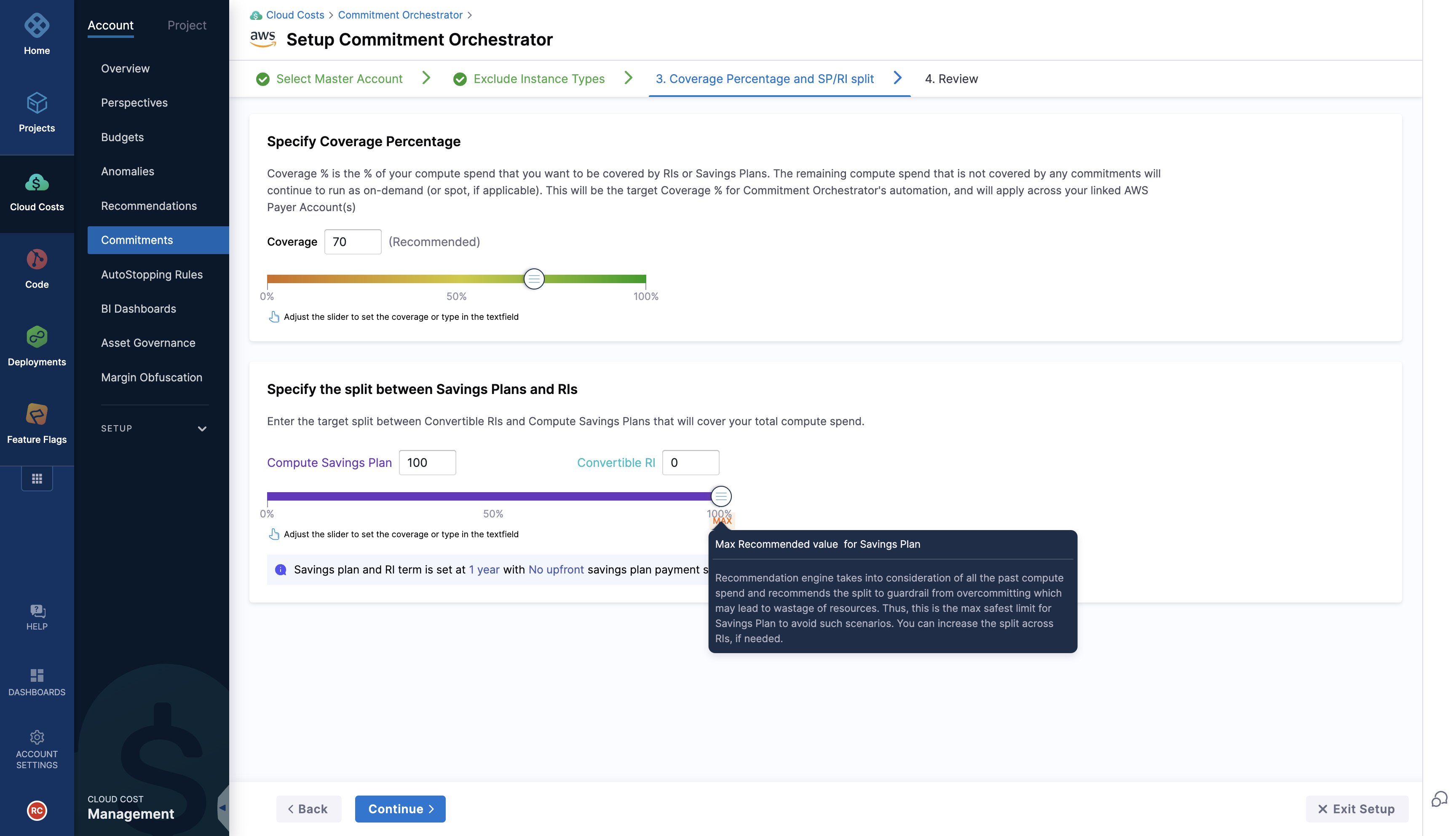
Step 3: Coverage Percentage and SP/RI split
Coverage Percentage: The Coverage percentage is the percentage of your compute spend that you want to be covered by Savings Plans or Reserved Instances. The remaining amount will continue to run as on-demand.
SP/RI split: Out of the totally compute spend, you have the option to split it between Convertible Reserved Instances and Compute Savings Plan. Out of total coverage, the system automatically calculates the maximum guardrail for purchasing the Savings Plans given the past compute spend data to ensure limiting any over purchase of saving plans. You can reduce the percentage by increasing share of Reserved Instances. However, you can't increase the coverage via Savings Plan beyond the max limit.
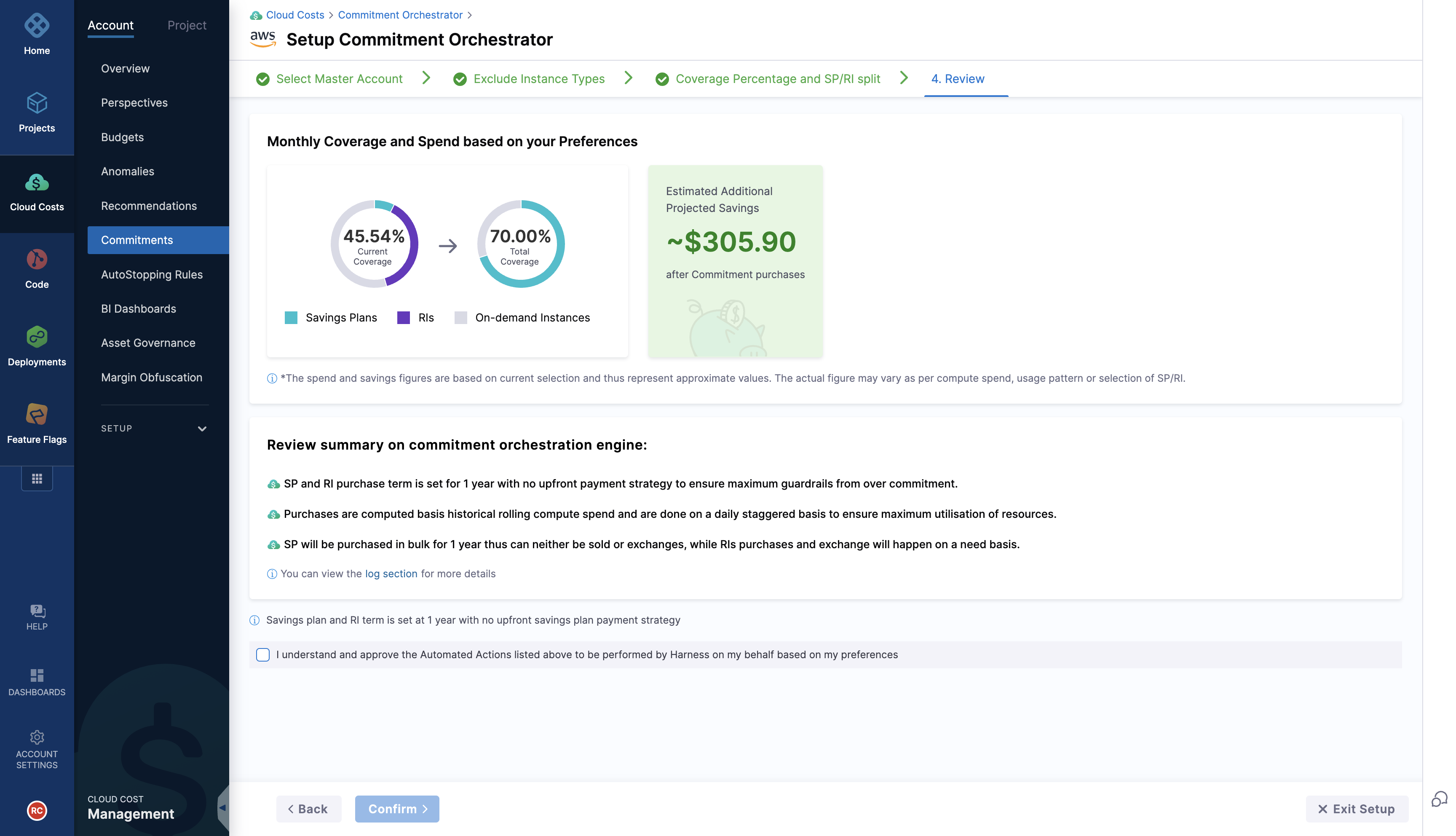
Step 4: Review
After all the set-up steps, you can review and finalise your inputs.
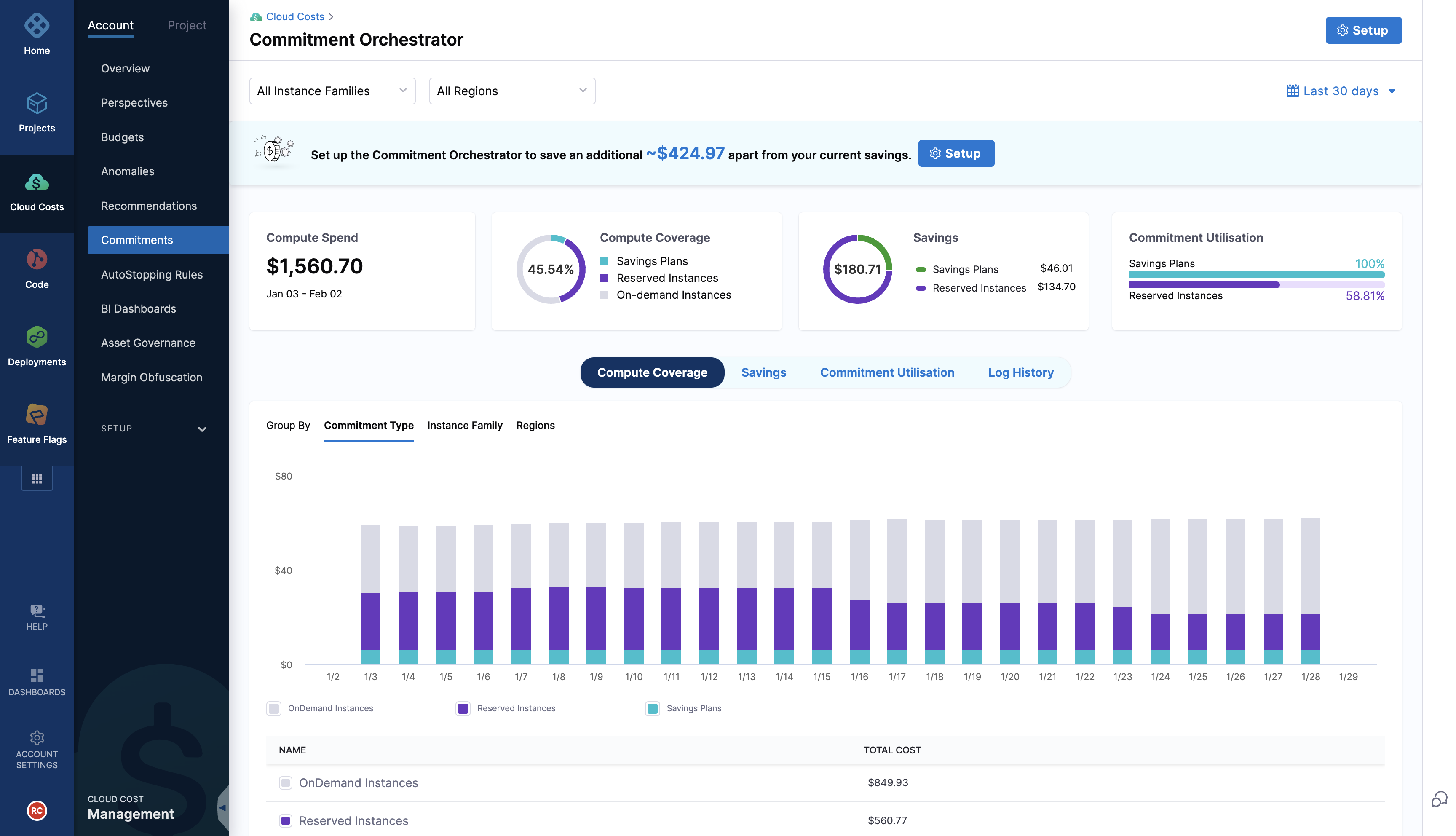
Post set-up, you can view your dashboard with all the information required . You can manipulate the information shown according to the filters such as Instances and Regions and see all the information related to Computer Coverage, Savings, Commitment Utilisation alongwith Log history. This way, the dashboard allows you to easily keep a track of your commitments and make informed decisions.
Steps to configure:
Step 1: Visibility
To enable visibility, in the master account connector, you need to add the following permissions.
"ec2:DescribeReservedInstancesOfferings",
"ce:GetSavingsPlansUtilization",
"ce:GetReservationUtilization",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypeOfferings",
"ce:GetDimensionValues",
"ce:GetSavingsPlansUtilizationDetails",
"ec2:DescribeReservedInstances",
"ce:GetReservationCoverage",
"ce:GetSavingsPlansCoverage",
"savingsplans:DescribeSavingsPlans",
"organizations:DescribeOrganization"
"ce:GetCostAndUsage"
Step 2: Setup flow (to enable actual orchestration)
"ec2:PurchaseReservedInstancesOffering",
"ec2:GetReservedInstancesExchangeQuote",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypeOfferings",
"ec2:AcceptReservedInstancesExchangeQuote",
"ec2:DescribeReservedInstancesModifications",
"ec2:ModifyReservedInstances"
"ce:GetCostAndUsage"
savingsplans:DescribeSavingsPlansOfferings
savingsplans:CreateSavingsPlan
Native User Approval
With this feature, users can approve the recommendations generated by the orchestrator. This feature enhances the functionality of the orchestrator by enabling user actions such as approval or rejection of recommendations generated by the engine.
Supported actions:
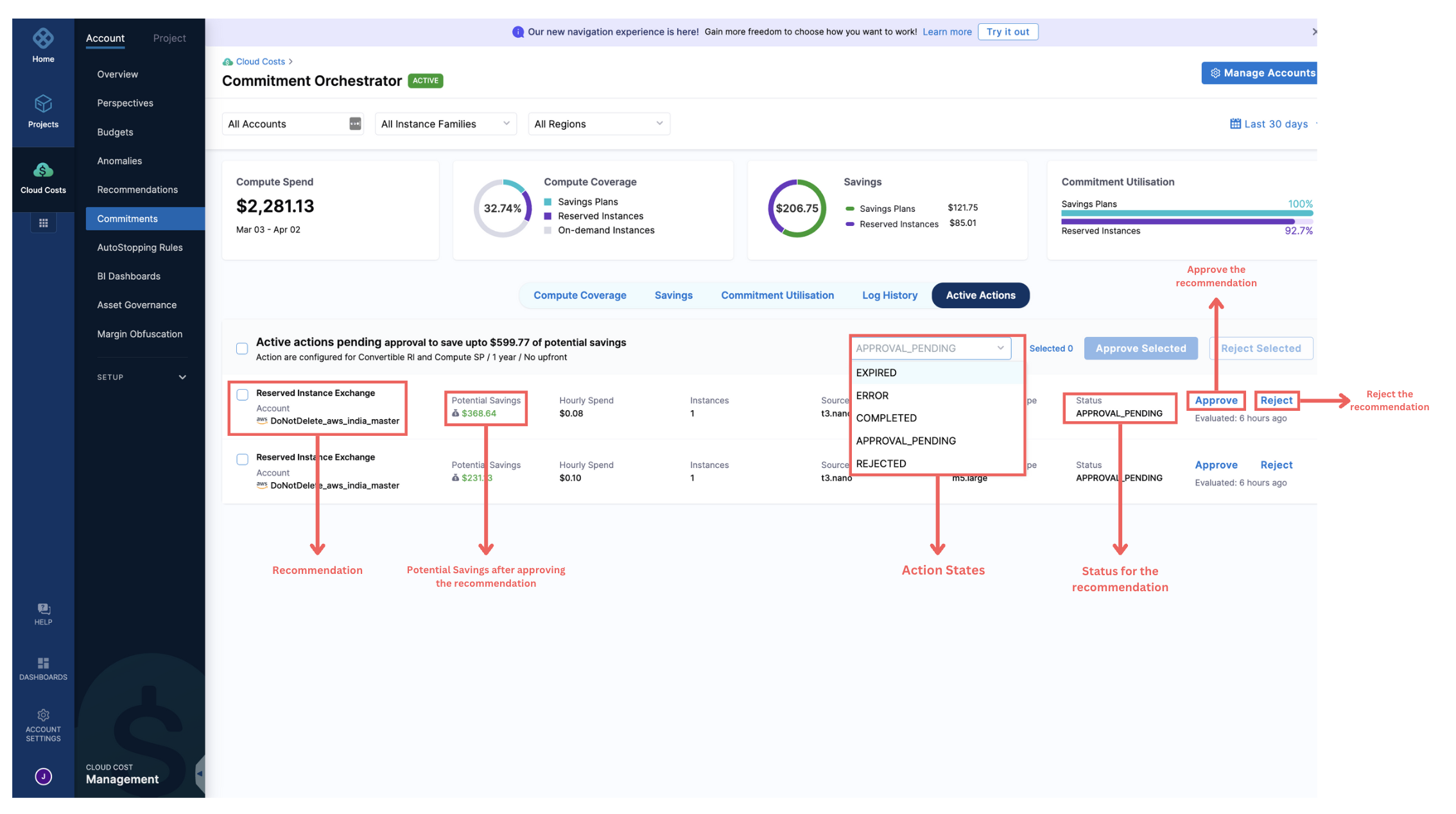
The Commitment Orchestrator supports six action states currently:
- APPROVED: You can approve the recommendation, allowing the action to proceed.
- REJECTED: You can choose to reject the recommendation, preventing the action from taking place.
- APPROVAL_PENDING: The action is pending approval by the user. This is the default state for all recommendations and any pending actions will expire in 24 hours.
- EXPIRED: The recommended action has expired.
- ERROR: The approval process encounters an error.
- COMPLETED: The approved recommendation has been successfully completed.
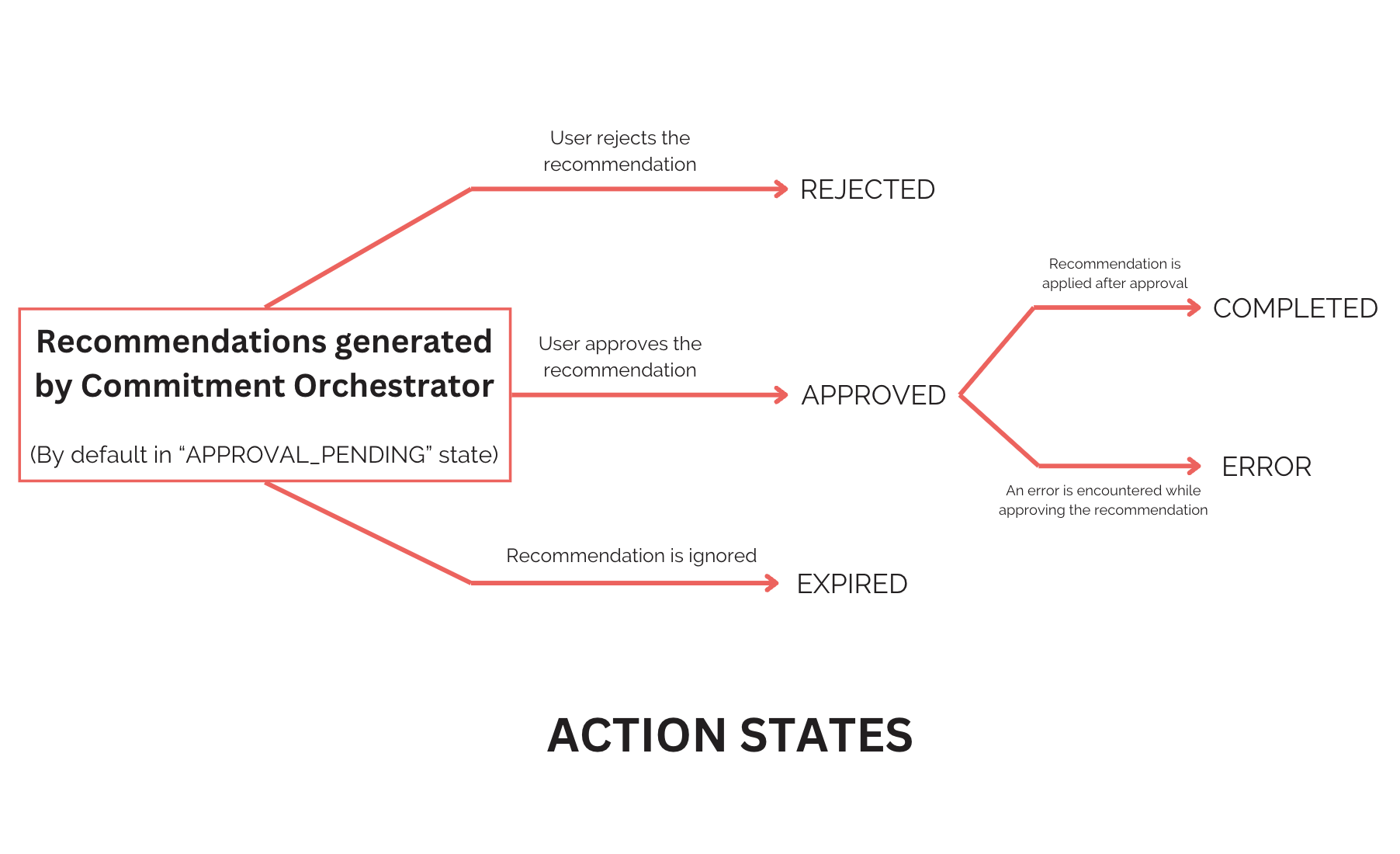
The Commitment Orchestrator facilitates the following:
-
SP Purchase Plan: We send out monthly recommendations for purchasing Compute SP (Savings Plans), provided there isn't an existing SP in place already. Upon receipt, you will have 24 hours to approve the request. If not approved within this timeframe, the recommendation will expire. However, rest assured that our systems will automatically regenerate the recommendation for your consideration.
-
RI Purchase Plan: Our system generates recommendations for purchasing Convertible Reserved Instances (RIs), multiple times throughout the month. Just like with Standard Purchase (SP) recommendations, you'll have a 24-hour window to approve these recommendations. Should you miss the window, new recommendations will be automatically generated to accommodate any changes in the compute spend. Additionally, if there are no existing AWS EC2 t3.nano RIs, a seed RI (t3.nano) will be purchased. If any other RI exists, we will leverage it to obtain a t3.nano to ensure that the t3.nano also expires along with the original RI.
-
RI Exchange Plan: If you're considering exchanging RI, our system provides recommendations that will be generated multiple times daily. Whether you choose to approve individual exchanges or group them, you have the flexibility to manage your resources efficiently. Just like with purchase plans, recommendations may change based on the compute spend variations, and if not acted upon within 24 hours, they will expire and be regenerated automatically.
Action Center UI
In the Action Center UI, you can:
- View a list of all recommendations generated by the engine, categorized by day and recommendation type.
- Approve or reject recommendations individually, in subsets, or all at once.
- Perform actions on different master accounts and regions.
You can change and select the mode (either automatic approval or manual approval) during the setup flow.
Beta features:
In its Beta phase, the Commitment Orchestrator provides:
- Enhanced Visibility: Commitment Orchestrator gives insight into current account status, including detailed breakdowns of savings and resource utilization across all accounts and regions. (Requires visibility permission as part of the master account connector setup).
- Convertible RI Support: It allows easy purchasing of Convertible Reserved Instances (RI) to optimize cost-efficiency and flexibility in resource allocation.
- Compute SP Purchase Support: Commitment Orchestrator streamlines the purchase of Compute Savings Plans (SP) to maximize cost savings while maintaining compute coverage.
- Convertible RI Exchange: With Commitment Orchestrator, Convertible Reserved Instances to adapt to changing workload demands and optimize commitment utilization.
- Commitment Orchestrator Setup: Commitment Orchestrator can be easily setup on your master account to centralize commitment management and streamline operations.
- Detailed Activity Logs: Harness’ Commitment Orchestrator also provides comprehensive logs detailing every action performed within the Commitment Orchestrator, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- RBAC Support: Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is included to manage permissions and access levels within the Commitment Orchestrator, enhancing security and governance.
| Persona | Scenario | Value Added |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Financial Manager/ Cloud Architect | A Cloud Financial Manager aims to maximize cost savings for the organization's AWS commitments and Cloud Architects are responsible for designing and overseeing the organization's cloud infrastructure with varying workloads | Cost optimization and Automated Purchase Management : Commitment Orchestrator assists the manager in optimizing commitment utilization, preventing overcommitment or underutilization, and ensuring maximum ROI on cloud expenditures. The Purchase Engine of Commitment Orchestrator, automated by Cloud Architects, streamlines the analysis of on-demand spend and purchases Reserved Instances or Savings Plans based on target coverage, ensuring efficient resource allocation. |
| Cloud Administrators | Cloud Administrators handle day-to-day cloud operations, including managing Convertible Reserved Instances. | Convertible RI Management: The Utilization Engine of Commitment Orchestrator, managed by Cloud Administrators, identifies underutilized Convertible RIs and performs conversions to increase utilization, optimizing resource usage and cost efficiency. |
| IT Managers | IT Managers need detailed insights into commitments, utilization, and savings across multiple accounts and regions. | Visibility and Reporting: Commitment Orchestrator provides visibility into account breakdowns, savings, and utilization, supporting IT Managers in making informed decisions about cloud commitments and expenditures |
| Organizations with multiple AWS accounts | Organizations with multiple AWS accounts seek flexibility in commitment management due to the ability to support multiple master accounts and set separate coverage for each of them. | Staggered Purchase to Prevent Overcommitment: Commitment Orchestrator's daily staggered purchases, orchestrated by administrators in multi-account structures, prevent overcommitments, ensuring financial flexibility and optimal resource allocation. |
FAQs
- Which cloud providers are supported at the moment?
--> Currently, we support AWS Compute Saving Plans and Convertible RIs for EC2.
- Is Audit trails support available?
--> In Beta version of CO, Audit trails are not supported but in upcoming GA release, it will be supported.
- How many Saving Plan purchases happen in a month?
--> Only 1 SP purchase happens on a month on the basis of the last rolling 12 months data.
- How many RI purchases happen in a month?
--> It's a daily staggered and recurring purchase, and hence, can happen multiple times.
- How many exchanges happen in a month?
--> Number of exchanges depends on the requirement of the user.
- Where can I see the history of all the actions taken?
--> In the visibility section, you can see all the actions under the logs
- Is RBAC supported?
--> Yes, as part of Beta there are two permissions : view(Visibility) and edit (Setup) 8. Can orchestration be setup on any account?
--> No, only master account with correct permission listed above will be allowed and at a time only one account can be set up.