CCM SaaS Architecture
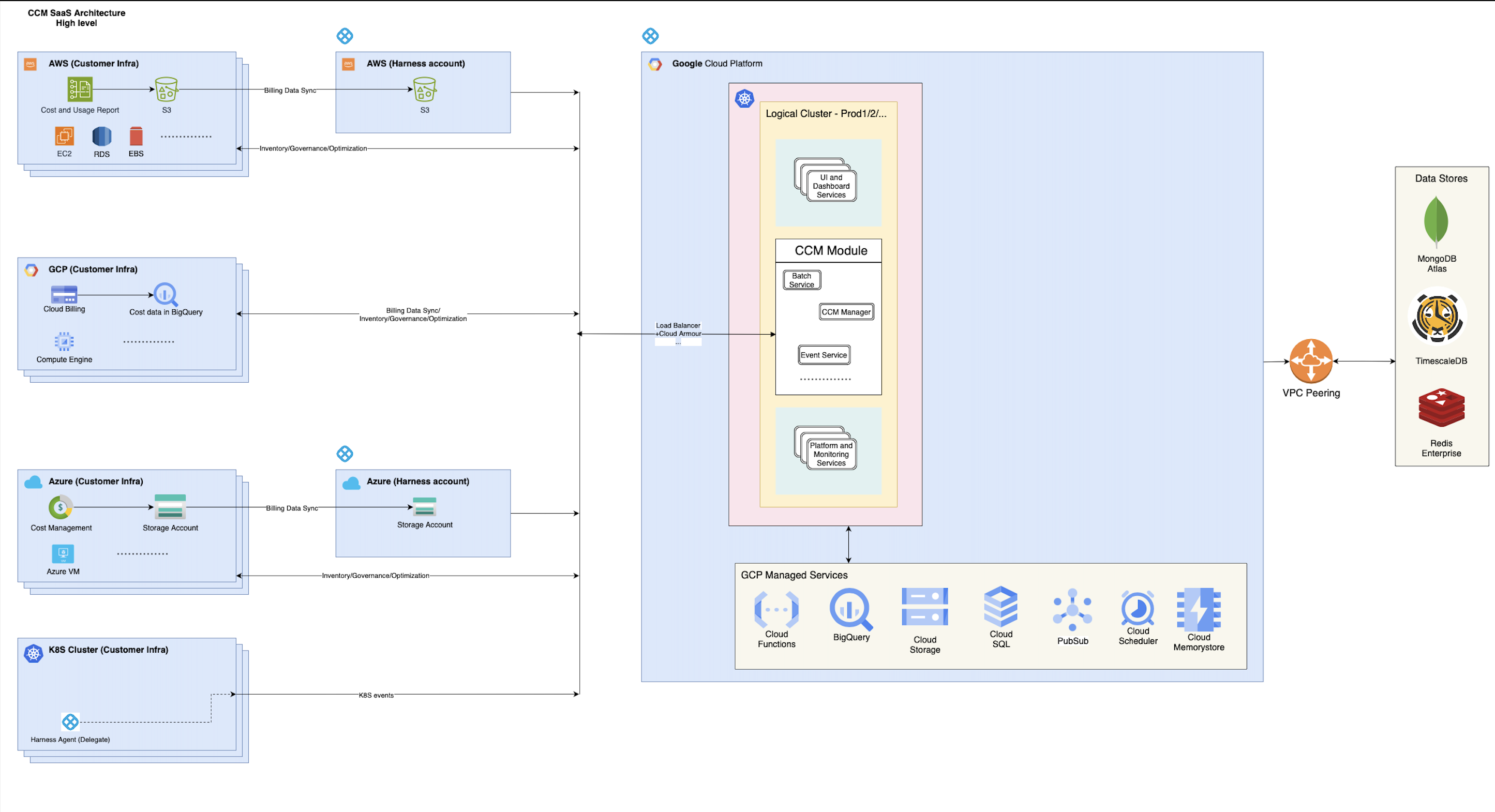
In this high-level overview of the CCM SaaS infrastructure, we delve into the inner workings of CCM as it performs crucial operations for cloud cost visibility and optimization across popular platforms such as K8S, AWS, GCP, and Azure.
At the core of CCM's architecture, a suite of microservices within the CCM Module handles diverse use cases and functionalities. These microservices manage background processing, API serving, and K8S event handling, among others.
The primary datastore driving CCM's Cost Visibility features is BigQuery, with additional support from CloudSQL, CloudMemorystore, MongoDB, Redis, and TimescaleDB. Complementing these datastores, CCM leverages various GCP managed cloud services including CloudFunctions, PubSub, Cloud Storage, and Cloud Scheduler.
Let's explore how CCM orchestrates operations on each cloud platform:
1. AWS
CCM periodically syncs Cost and Usage Reports (CUR) from the source S3 bucket to the Harness S3 bucket. Following this, it conducts backend processing and stores the data in BigQuery. For functionalities like Cloud Asset Inventory, Asset Governance, and AutoStopping, CCM interacts with the respective AWS APIs (e.g., EC2, RDS), also retrieves utilization data for generating impactful recommendations on hard dollar savings.
2. GCP
Cost data on GCP resides in a BigQuery table at the source, which CCM syncs to a destination BigQuery table owned by Harness. Similar to AWS, backend processing follows, supporting various use cases. Cloud Asset Inventory, Asset Governance, and AutoStopping involve interactions with GCP APIs for supported resource types like Compute Engine etc.
3. Azure
Azure's cost data is initially stored in a source storage account, synced to a destination storage account owned by Harness. Subsequent backend processing culminates in storing the data in BigQuery in diverse formats. For functionalities like Cloud Asset Inventory, Asset Governance, and AutoStopping, CCM communicates with Azure APIs (e.g., Azure VM) and retrieves utilization data to drive recommendations for hard dollar savings.
4. K8S
In the realm of Kubernetes cost visibility, CCM extracts information through various K8S events. This is achieved by periodically pulling data via metrics server and direct calls to K8S APIs. Facilitated by a lightweight agent (delegate) installed in the source cluster, these events are sent to Harness via HTTP and consumed by backend jobs. The processed data finds its way into TimescaleDB and BigQuery. Utilization data is also fetched, aiding CCM in generating recommendations for nodepool and workload optimizations, leading to tangible hard dollar savings.
This detailed exploration showcases how CCM seamlessly integrates with different cloud platforms, employing tailored strategies for each, and providing valuable insights for effective cloud cost management.