Upload Artifacts to JFrog
Use the Upload Artifacts to JFrog Artifactory step in your CI pipelines to upload artifacts to JFrog Artifactory non-Docker registries. To upload artifacts to a JFrog Docker registry, use a script in a Run step.
To configure this step, you need access to a JFrog Artifactory instance with a non-Docker registry.
Prepare artifacts to upload
The Upload Artifacts step needs artifacts to upload. Make sure your CI pipeline has steps that generate artifacts to upload, such as build artifacts, output generated from scripts, test reports from running tests, or anything else you want to upload to JFrog. The steps you use depend on the artifacts you want to upload.
Add the Upload Artifacts step
Add the Upload Artifacts to JFrog Artifactory step to your pipeline's Build stage.
- step:
type: ArtifactoryUpload
name: ArtifactoryUpload_1
identifier: ArtifactoryUpload_1
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_ARTIFACTORY_CONNECTOR_ID
target: groupId/artifactId/version
sourcePath: path/to/source
The Upload Artifacts to JFrog Artifactory step has the following settings. Depending on the build infrastructure, some settings might be unavailable or optional.
Name, Description, Tags
- Name: A name for the step. Harness automatically assigns an ID (Entity Identifier) based on the Name. You can change the ID until the step is saved, then it is locked.
- Description and Tags: Optional metadata.
Artifactory Connector
Select the Harness Artifactory connector to use for this upload. The JFrog Account associated with the connector must have read/write permission.
This step supports Artifactory connectors that use either anonymous or username and password authentication.
If the connector uses username and password authentication, the PLUGIN_USERNAME and PLUGIN_PASSWORD used by this step are derived from the selected Artifactory connector.
Target, Source Path
The Target is the target path in the JFrog Artifactory registry. This is a target repository name relative to the server URL in the connector. If pom.xml is not present, then the Target must be a full path to an artifacts folder, such as groupId/artifactId/version.
Source Path is a path, relative to the stage workspace, to the artifact file/folder that you want to upload. The root stage workspace directory is /harness.
If you want to upload a compressed file, you must use a Run step to compress the artifact before uploading it.
JFrog CLI flags
You can use stage variables to pass the following optional flags supported by the JFrog CLI:
-
PLUGIN_BUILD_NAME: Specify the name of the build associated with the uploaded artifacts in JFrog Artifactory. Use this flag to organize and track artifacts by their build name.variables:
- name: PLUGIN_BUILD_NAME
type: String
description: "Name of the build associated with the uploaded artifacts in JFrog"
required: false
value: <+pipeline.name> # You can use an expression or a fixed value. -
PLUGIN_BUILD_NUMBER: Specify the build number associated with the uploaded artifacts in JFrog Artifactory. Use this flag to version and identify different builds of the same project or component.variables:
- name: PLUGIN_BUILD_NUMBER
type: String
description: "Build number associated with the uploaded artifacts in JFrog"
required: false
value: <+pipeline.executionID> # You can use an expression or a fixed value.
Use the Artifactory Drone plugin
The built-in Upload Artifacts to JFrog Artifactory step uses the Artifactory Drone plugin. If you don't (or can't) use the built-in step, you can also run this plugin directly in a Plugin step. You might need to do this if there is a particular configuration or flag that is not supported by the way the plugin is used in the built-in step.
The settings are declared slightly differently when using a Plugin step, but you can still pass the --build-name and --build-number flags when using a Plugin step. For example:
- step:
type: Plugin
name: plugin
identifier: plugin
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
image: plugins/artifactory
settings:
access_token: YOUR_JFROG_TOKEN
url: YOUR_JFROG_ARTIFACTORY_URL
source: /path/to/source
target: /path/to/target
build_name: <+pipeline.name> # You can use an expression or a fixed value.
build_number: <+pipeline.executionID> # You can use an expression or a fixed value.
targetProps: key1=123;projectName=ExampleApp # Optional metadata/properties
Additional container settings
Settings specific to containers are not applicable when using the step in a stage with self-managed VM or Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
Run as User
Specify the user ID to use to run all processes in the pod if running in containers. For more information, go to Set the security context for a pod.
Set container resources
Set maximum resource limits for the resources used by the container at runtime:
- Limit Memory: The maximum memory that the container can use. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point number using the suffixes
GorM. You can also use the power-of-two equivalentsGiandMi. The default is500Mi. - Limit CPU: The maximum number of cores that the container can use. CPU limits are measured in CPU units. Fractional requests are allowed; for example, you can specify one hundred millicpu as
0.1or100m. The default is400m. For more information, go to Resource units in Kubernetes.
Timeout
Set the timeout limit for the step. Once the timeout limit is reached, the step fails and pipeline execution continues. To set skip conditions or failure handling for steps, go to:
View artifacts on the Artifacts tab
You can use the Artifact Metadata Publisher plugin to publish artifacts to the Artifacts tab. To do this, add a Plugin step after the Upload Artifacts to JFrog Artifactory step.
- Visual
- YAML
Configure the Plugin step settings as follows:
- Name: Enter a name.
- Container Registry: Select a Docker connector.
- Image: Enter
plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher. - Settings: Add the following two settings as key-value pairs.
file_urls: Provide a URL to the artifact that was uploaded in the Upload Artifacts to JFrog Artifactory step. If you uploaded multiple artifacts, you can provide a list of URLs.artifact_file: Provide any.txtfile name, such asartifact.txtorurl.txt. This is a required setting that Harness uses to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.
Add a Plugin step that uses the artifact-metadata-publisher plugin.
- step:
type: Plugin
name: publish artifact metadata
identifier: publish_artifact_metadata
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage
image: plugins/artifact-metadata-publisher
settings:
file_urls: https://complete/url/to/artifact/on/jfrog
artifact_file: artifact.txt
connectorRef: Use the built-in Docker connector (account.harness.Image) or specify your own Docker connector.image: Must beplugins/artifact-metadata-publisher.file_urls: Provide the URL to the artifact that was uploaded in the Upload Artifacts to JFrog Artifactory step. If you uploaded multiple artifacts, you can provide a list of URLs.artifact_file: Provide any.txtfile name, such asartifact.txtorurl.txt. This is a required setting that Harness uses to store the artifact URL and display it on the Artifacts tab. This value is not the name of your uploaded artifact, and it has no relationship to the artifact object itself.
Build logs and artifact files
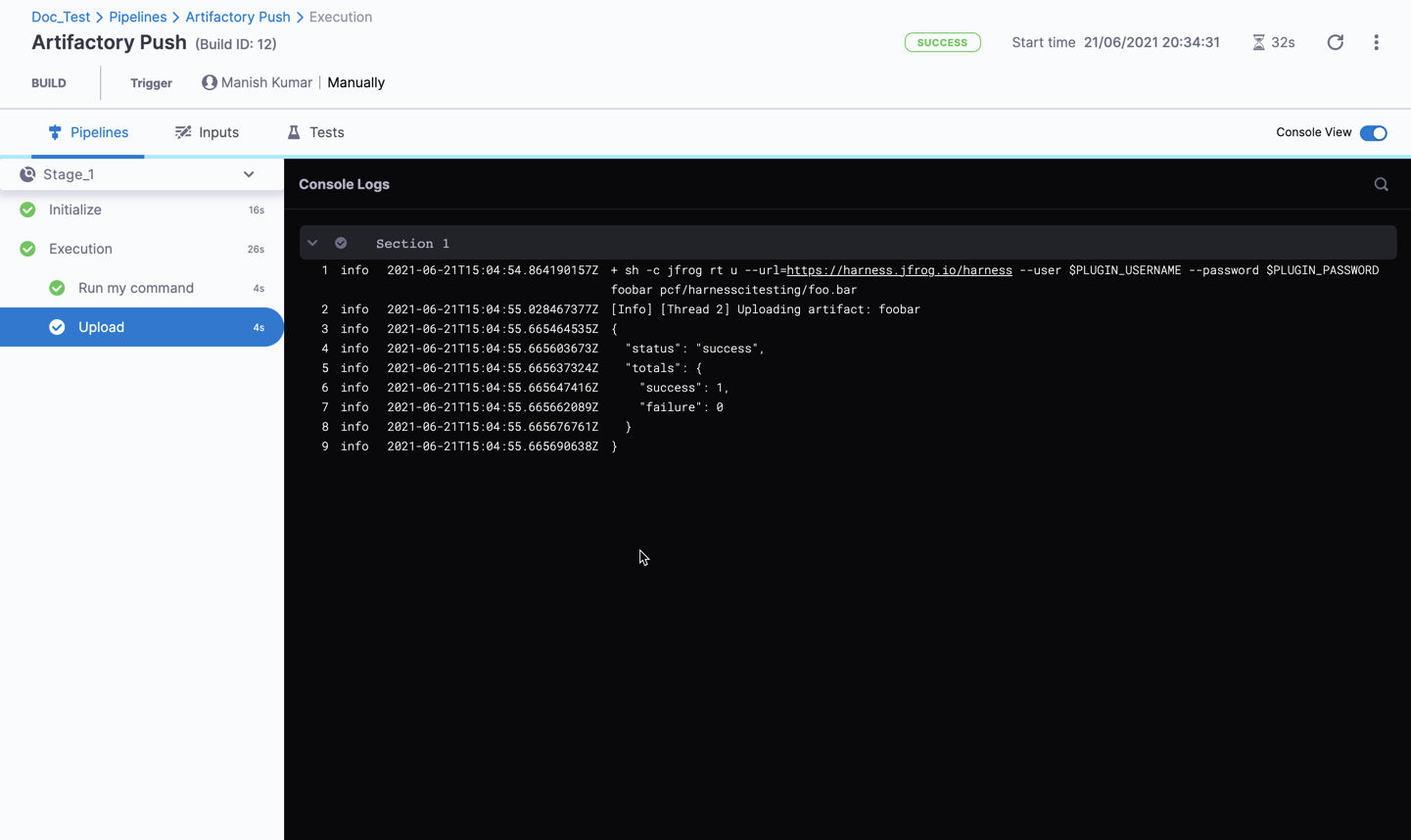
When you run the pipeline, you can observe the step logs on the build details page.
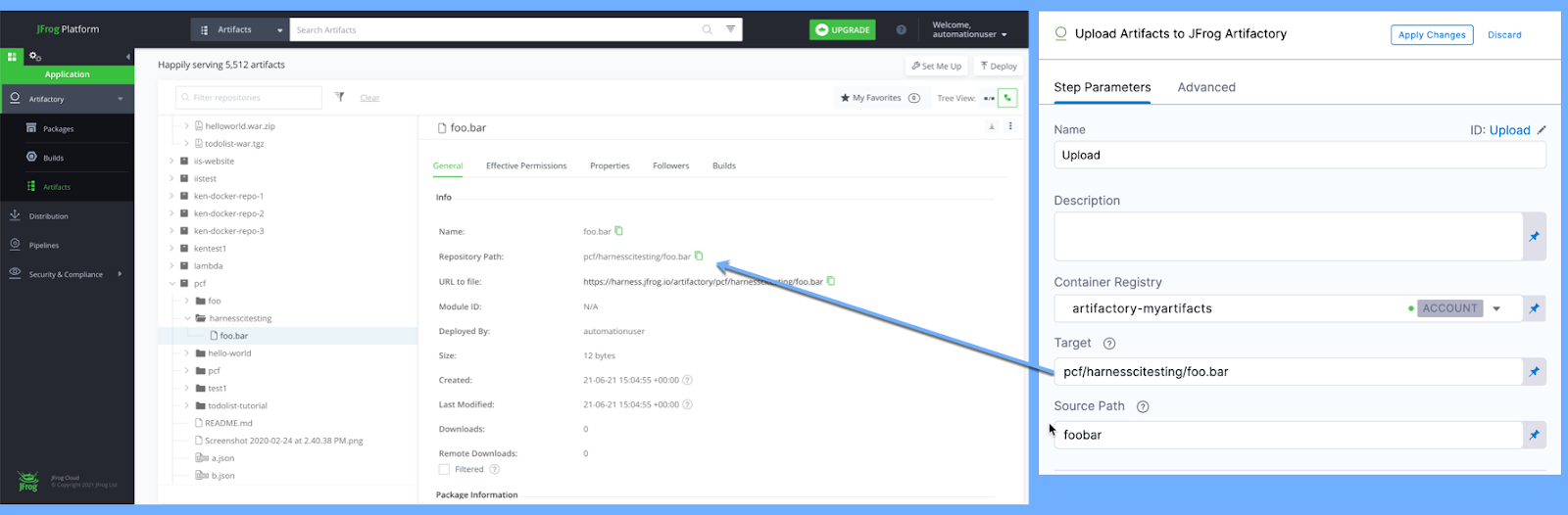
If the Upload Artifacts step succeeds, you can find the artifact in your JFrog repo.
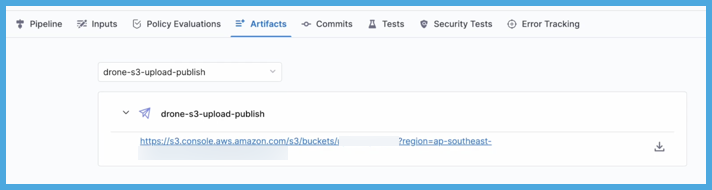
If you used the Artifact Metadata Publisher, you can find a link to the artifact on the Artifacts tab.
On the Artifacts tab, select the step name to expand the list of artifact links associated with that step.
If your pipeline has multiple steps that upload artifacts, use the dropdown menu on the Artifacts tab to switch between lists of artifacts uploaded by different steps.
Troubleshoot uploading artifacts
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related uploading artifacts, such as: