Linux network latency
Linux network latency injects chaos to disrupt network connectivity in linux machine by adding delay to the network requests.
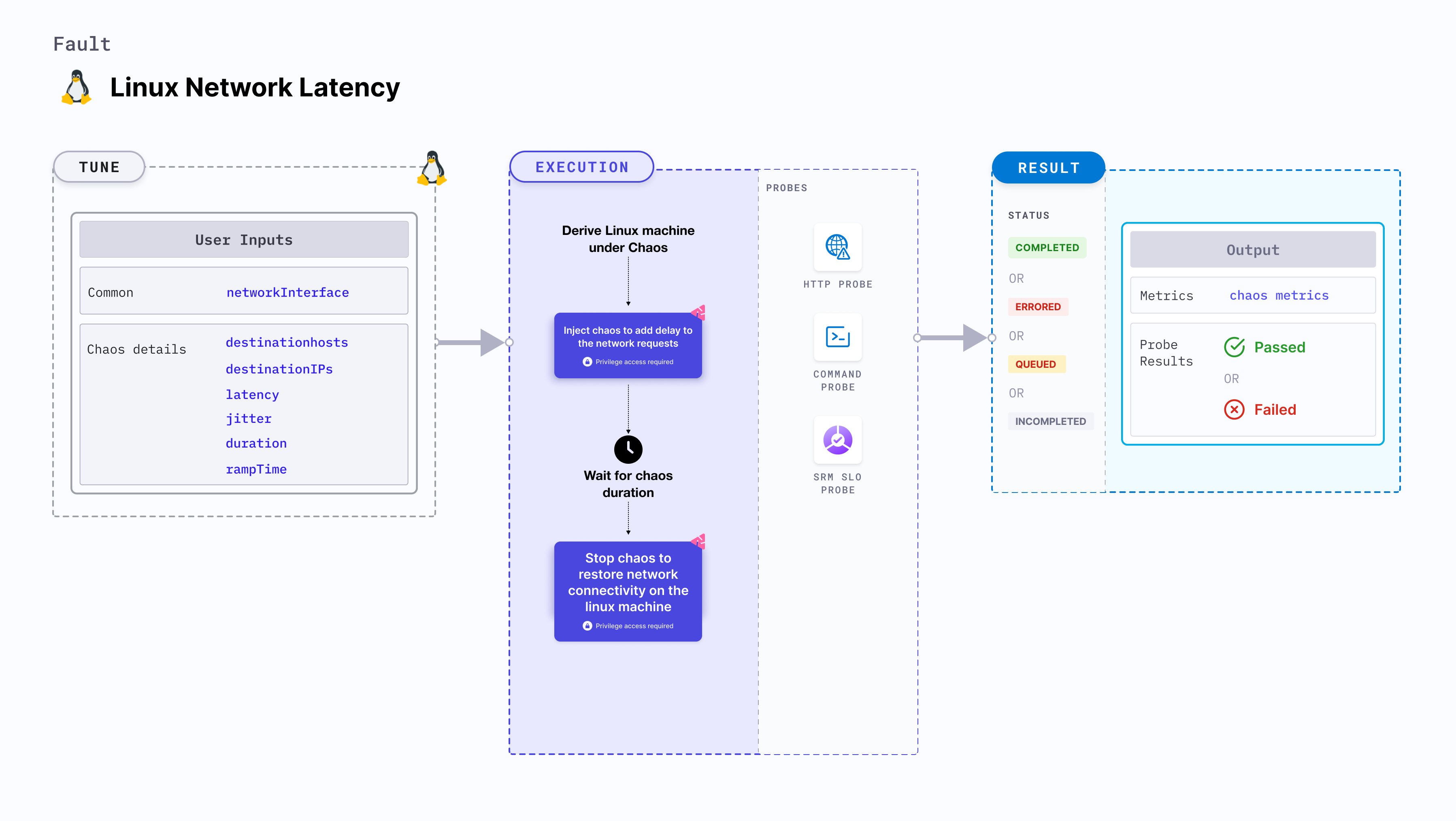
Use cases
- Induces network latency on the target Linux machines.
- Simulates latency in connectivity access by delaying the network requests of the machine.
- This fault can be executed on Ubuntu 16 or higher, Debian 10 or higher, CentOS 7 or higher, RHEL 7 or higher, Fedora 30 or higher, and openSUSE LEAP 15.4 or higher.
- The
linux-chaos-infrastructuresystemd service should be in an active state, and the infrastructure should be inCONNECTEDstate.
Fault permissions
The fault uses the root Linux user and root user group.
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| networkInterfaces | Network interfaces to target as comma separated values. | For example: eth0,ens192 |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| destinationHosts | List of the target host names or keywords. For example: google.com,litmuschaos.io | If neither destinationHosts and destinationIPs is provided, all host names/domains will be targeted |
| destinationIPs | List of comma- separated target IPs. Also supports a list of target destination ports for a given IP, that are separated by a pipe (|). For example, 1.1.1.1,35.24.108.92|3000|8080. | If neither destinationHosts and destinationIPs is provided, all host names/domains will be targeted |
| latency | Amount of latency to added to connection in ms. For example: 2000 | Defaults to 2000 |
| jitter | Amount of jitter to be added in ms. Jitter will define the max randomized deviation from the provided latency value. For example: 100 | Defaults to 0 |
| duration | Duration through which chaos is injected into the target resource. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 30s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s |
| rampTime | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 0s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s |
Destination hosts
The destinationHosts input variable subjects the comma-separated names of the target hosts to chaos.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-network-latency
labels:
name: network-latency
spec:
networkChaos/inputs:
destinationHosts: 'google.com'
networkInterfaces: "eth0"
Destination IPs
The destinationIPs input variable subjects the comma-separated names of the target IPs to chaos. You can specify the ports to be targeted for an IP by using a pipe (|) as a separator. While providing ports is optional, omitting them will affect all the ports associated with the destination IPs.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-network-latency
labels:
name: network-latency
spec:
networkChaos/inputs:
destinationIPs: '1.1.1.1,192.168.5.6|80|8080'
networkInterfaces: "eth0"
Latency and jitter
The latency and jitter input variables add delay and a small deviation to the delay, respectively, with respect to the connection.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this input variable:
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: linux-network-latency
labels:
name: network-latency
spec:
networkChaos/inputs:
latency: "1000"
jitter: "200"
networkInterfaces: "eth0"