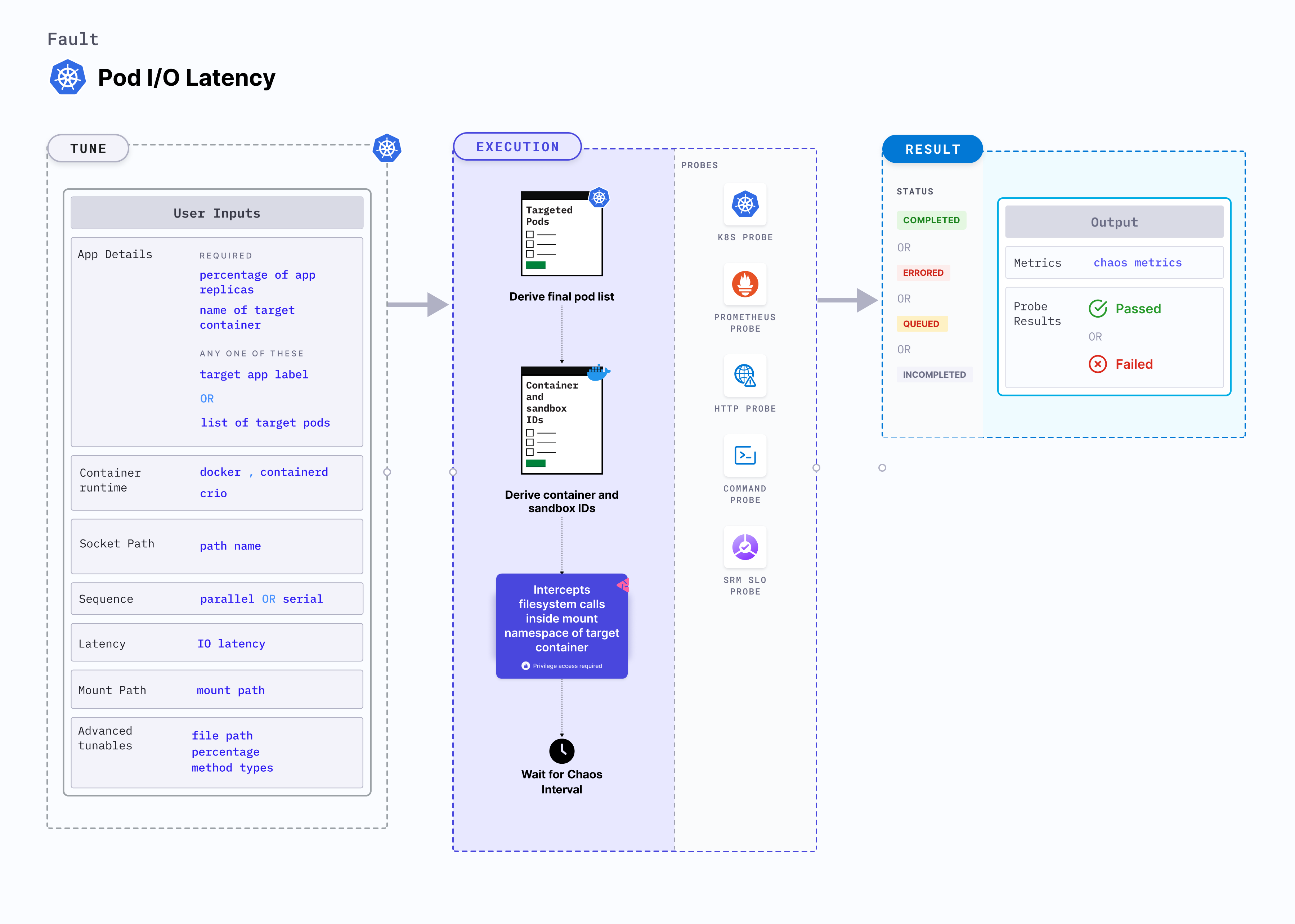
Pod IO latency
Pod IO latency simulates slow I/O operations by introducing delays in system calls of the files located within the mounted volume of the pod. This fault is used for testing the resilience, performance, and scalability of the pod. This can help identify performance bottlenecks, test the system's ability to handle high loads, and evaluate its behavior in high-stress scenarios.
Use cases
Pod IO latency:
- Simulates the slow file system calls, which can be used to test the resilience of an application or system to slow I/O performance.
- Simulates the system's behavior when dealing with increased I/O operations. This can help identify any issues that may arise when the system is under high load.
- Tests the system performance during backup or recovery operations, it is possible to see how the system handles slow I/O performance and ensure that backups and recoveries are successful under all conditions.
- Simulates the slow file system calls under different loads, helping to identify the optimal capacity of the system to ensure that it can handle the expected load without experiencing performance issues.
- Due to the large blast radius of this fault, we recommend you do not execute it in the production environment.
- Through the fault execution, the application pod can potentially fail to perform successful IO writes if the
writesystem call is being targeted. This can cause any data produced in this duration to be lost. - Any data produced before the execution of the fault is not harmed as a result of its execution.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes > 1.16
- The application pods should be in the running state before and after injecting chaos.
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| LATENCY | Specify the latency to be injected in file system calls | Accepts any unit of time, for example, 60s, 1m, or 60000ms. For more information, go to latency. |
| MOUNT_PATH | The absolute mount path of the volume mounted to the target pod | For more information, go to mount path. |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TARGET_CONTAINER | Name of the container subject to IO latency | If the value is not provided, the fault injects chaos on the first container of the pod. For more information, go to target specific container. |
| NODE_LABEL | Node label used to filter the target node if TARGET_NODE environment variable is not set. | It is mutually exclusive with the TARGET_NODE environment variable. If both are provided, the fault uses TARGET_NODE. For more information, go to node label. |
| FILE_PATH | The path for injecting faults can be specified as either a single file or a wildcard. If not provided, it will target all the files present inside the mount path | For more information, go to file path. |
| PERCENTAGE | The likelihood of failure per operation, expressed as a percentage | For more information, go to percentage. |
| METHOD_TYPES | This contains the file system call or methods. | For more information, go to percentage. |
| CONTAINER_RUNTIME | Container runtime interface for the cluster | Default: containerd. Supports docker, containerd and crio. For more information, go to container runtime. |
| SOCKET_PATH | Path of the containerd or crio or docker socket file | Defaults to /run/containerd/containerd.sock. For more information, go to socket path. |
| LIB_IMAGE | Image used to inject chaos. | Default: chaosnative/chaos-go-runner:main-latest. For more information, go to image used by the helper pod. |
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration to inject chaos (in seconds) | Default: 60 s. For more information, go to duration of the chaos. |
| TARGET_PODS | Comma-separated list of application pod names subject to pod IO latency | If not provided, the fault selects target pods randomly based on provided appLabels. For more information, go to target specific pods. |
| PODS_AFFECTED_PERC | Percentage of total pods to target. Provide numeric values. | Default: 0 (corresponds to 1 replica). For more information, go to pod affected percentage. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds) | For example, 30 s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
| SEQUENCE | Sequence of chaos execution for multiple target pods | Default: parallel. Supports serial and parallel. For more information, go to sequence of chaos execution. |
IO latency
IO Latency to be injected in system calls of the files located within the mounted volume of the pod. Tune it by using the LATENCY environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects io latency in the file system calls
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-io-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# io latency
- name: LATENCY
value: '2s'
- name: MOUNT_PATH
value: '/etc/config'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
value: '60'
Mount path
Mount path of the volume mounted to the target application. Tune it by using the MOUNT_PATH environment variable.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects io latency in the file system calls
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-io-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# mount path of the volume
- name: MOUNT_PATH
value: '/etc/config'
- name: LATENCY
value: '2s'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
value: '60'
Advanced fault tunables
FILE_PATH: The path for injecting faults can be specified as either a single file or a wildcard. By default it targets all the files present inside the mount path.PERCENTAGE: The likelihood of failure per operation, expressed as a percentage. Default is 100%.METHOD_TYPES: This contains the file system call or methods. By default it targets all the methods.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# it injects io latency in the file system calls
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-io-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# filter the target files
- name: FILE_PATH
value: '/etc/config/file.txt'
# percentage of i/o calls
- name: PERCENTAGE
value: '50'
# names of the io methods
- name: METHOD_TYPES
value: '["read","write"]'
- name: LATENCY
value: '2s'
- name: MOUNT_PATH
value: '/etc/config'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
value: '60'
Container runtime and socket path
The CONTAINER_RUNTIME and SOCKET_PATH are environment variables to set the container runtime and socket file path, respectively.
CONTAINER_RUNTIME: This supportsdocker,containerd, andcrioruntimes. The default value iscontainerd.SOCKET_PATH: This contains path of containerd socket file by default(/run/containerd/containerd.sock). Fordocker, specify the path as/var/run/docker.sock. Forcrio, specify the path as/var/run/crio/crio.sock.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of these environment variables:
## provide the container runtime and socket file path
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: ChaosEngine
metadata:
name: engine-nginx
spec:
engineState: "active"
annotationCheck: "false"
appinfo:
appns: "default"
applabel: "app=nginx"
appkind: "deployment"
chaosServiceAccount: litmus-admin
experiments:
- name: pod-io-latency
spec:
components:
env:
# runtime for the container
# supports docker, containerd, crio
- name: CONTAINER_RUNTIME
value: 'containerd'
# path of the socket file
- name: SOCKET_PATH
value: '/run/containerd/containerd.sock'
- name: LATENCY
value: '2s'
- name: MOUNT_PATH
value: '/etc/config'
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
VALUE: '60'